- 1. Key Takeaway
- 2. Why Businesses Need PA, PG Solution - Facts and Figures to Know
- 3. What is a Payment Gateway?
- 4. What is a Payment Aggregator?
- 5. What Are the Key Differences Between a Payment Aggregator and a Payment Gateway?
- 6. How Each Model Works in the Payment Flow
- 7. Business Perspective, Which is Right for You?
- 8. What Are The Best Practices for Enterprise Payment Strategy
- 9. What Are the Compliance and Security Differences
- 10. Pricing and Cost Comparison
- 11. Integration and Technical Aspects
- 12. FAQs: Quick Answers
- 13. Final Thoughts
Have you ever wondered why online payment service providers call themselves payment aggregators, and others payment gateways?
Connecting for a payment solution for your business, you may have come across the term payment aggregator vs. payment gateway. What exactly is it?
Both terms differ from each other when it comes to processing a transaction. The fundamental difference in an aggregator is that it acts as an interface that handles the entire payment process for the merchant. On the other side, payment gateways provide a technology to facilitate the secure transfer of payment data.
In this complete guide, founders and startups can gather helpful insights into what a payment gateway is vs. a payment aggregator - along with the clarity for their features, compliances, pricing, and you will learn how to use the right solution for your organization.
Let’s drill down!
Key Takeaway
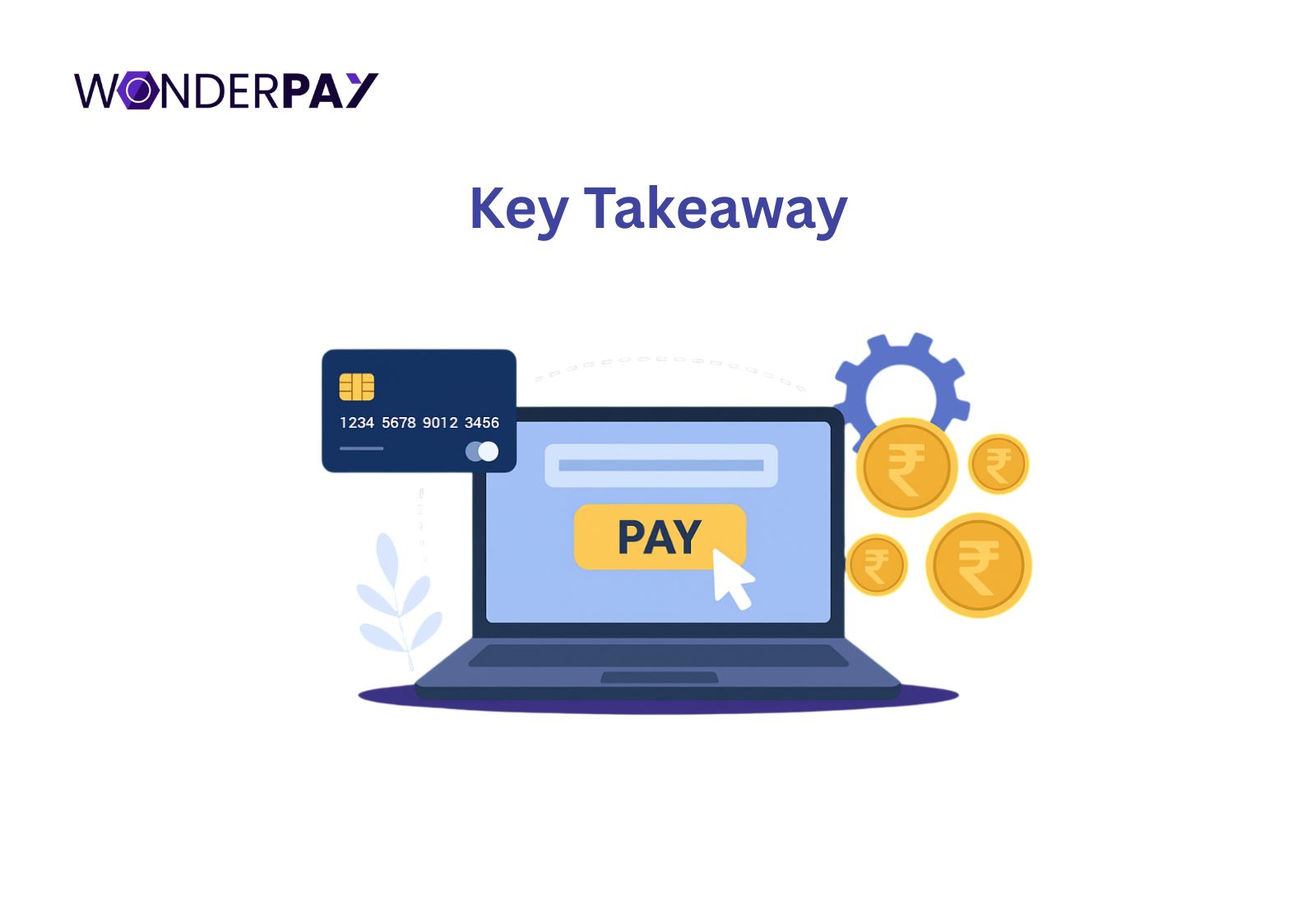
- A payment aggregator provides a single merchant account for businesses to accept payments, handles funds and settles transactions, while a payment gateway is a technology that securely transmits payment data between a business customers, and a payment processor.
| Criteria | Payment Gateway | Payment Aggregator | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology that securely transmits payment data between the customer, bank, and merchant. | An entity that allows multiple merchants to accept payments under its own merchant account. | |
| Function | Acts as a technical bridge for transaction processing. | Acts as a business facilitator handling onboarding, settlement, and risk. | |
| Onboarding | Requires individual merchant account setup and bank approvals. | Instant onboarding, no separate merchant account needed. | Startups, small sellers |
| Settlement | Directly to the merchant’s account from the acquiring bank. | Routed through the aggregator’s pooled account, then settled to the merchant. | SMBs & marketplaces |
| Regulatory Scope | Merchants must maintain PCI DSS compliance and work with acquirer banks. | Aggregators follow RBI’s PAPG authorization and handle compliance for sub-merchants. | Low-compliance teams |
| Customization | High full API control and routing options. | Moderate ready-to-use checkout and dashboards. | Enterprises & SaaS |
| Cost | Lower MDR at scale, but higher setup cost. | Slightly higher MDR, zero setup cost. | Growing businesses |
Why Businesses Need PA, PG Solution - Facts and Figures to Know
 India’s digital payments landscape has experienced rapid growth in a few years.
India’s digital payments landscape has experienced rapid growth in a few years.
Here are the clear figures and facts. A business should consider and get to know how this will enhance its revenue in the fast-changing payments era.
-
Digital payments are projected to expand more than three times from 159 billion transactions in Financial Year (FY) 2023-24 to 481 billion by FY 2028-29.
-
In terms of value for payment transactions, the market will double, from INR 265 trillion to INR 593 trillion, while being in the same period.
-
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) recorded 50% growth in FY 2023-24.
-
The merchant acquiring solutions, including online and offline, such as QRs, payment, also experience more than 25% growth.
-
Use of credit cards grew by approximately 20% because of demand from the Gen-Z population in Tier 2 and below locations.
-
Bharat Bill Payments solution (BBPS) saw growth by 25%. It was largely driven by new billers as well as increased payment options by virtual third-party application providers (TPAPs).
-
National Electronic Toll Collection experiences a continuous adoption growth of 10% by new vehicles.
This significant data indicates the need for a reliable payment system for businesses in India. In order to fulfill the gap for their business’s electronic transactions and increase the continuous revenue generation.
What is a Payment Gateway?
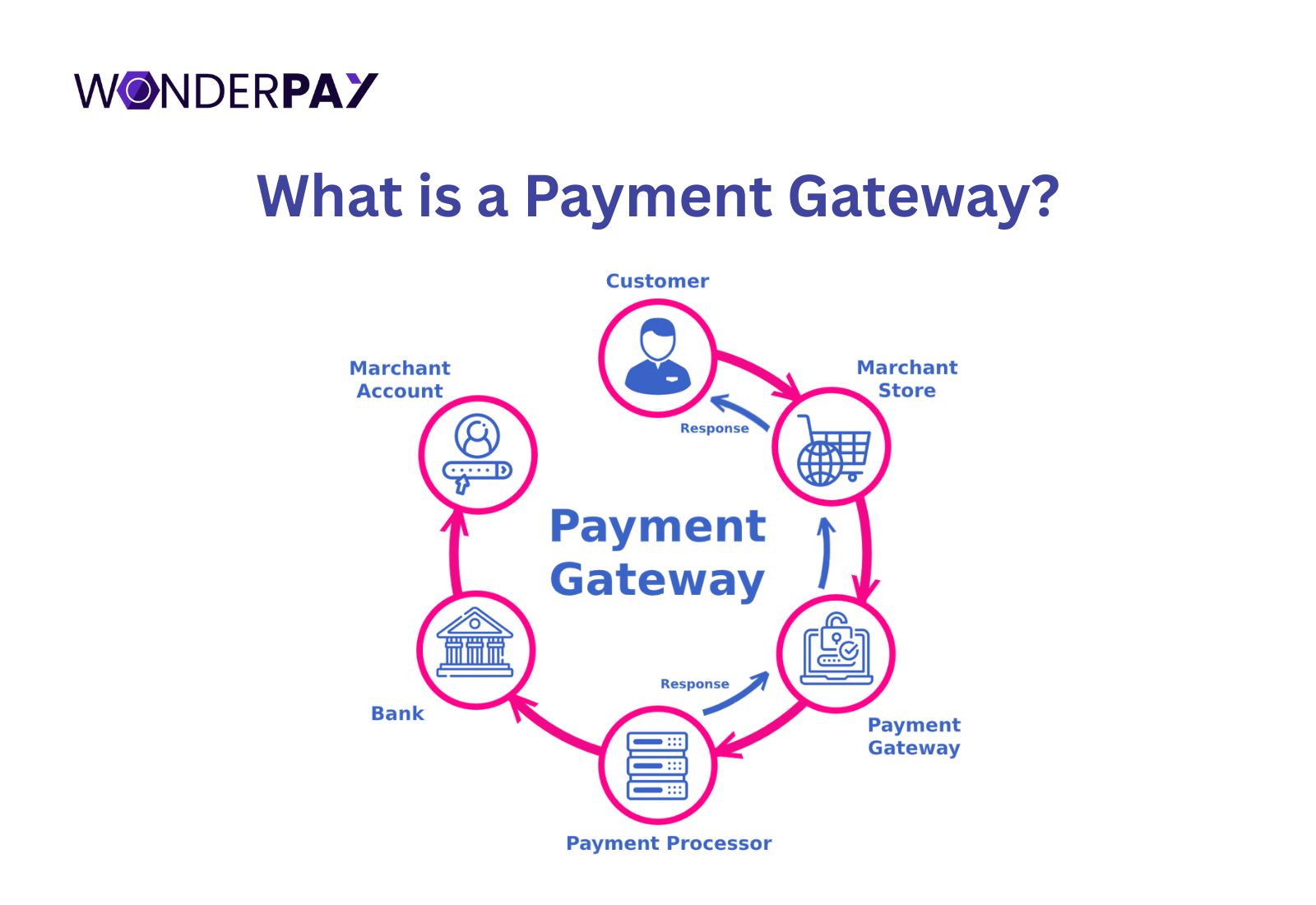
It is a technology that works as a bridge between businesses and banks for a digital transaction. A gateway facilitates online and in-person electronic payments. It captures and securely transmits customer payment information for authorization and fund settlement.
A PG receives payment information filled by customers, sends it to the payment processor, to communicates with relevant banks to get authorization or decline the transaction, which is done based on the filled payment information and the sufficient balance.
If the information is accurate and has sufficient balance. The payment will be approved and securely transferred to the business account without exposing customer sensitive information, like saving credit or debit card numbers. It is fully secured! Thanks to compliance like Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS).
A payment gateway comes with built-in security practices to protect customers and avoid fraud. Its encryption protects sensitive data using advanced algorithms, and features like tokenization replace customer card information with unique tokens, which eliminate unauthorized access.
What is a Payment Aggregator?

A payment aggregator (PA) is a service provider. It enables merchants to accept online payments through all online payment methods, including UPI, net banking, digital wallets, etc. It does not need to set up a separate merchant account, as it routes transactions via a single master account.
It offers a simplified solution for onboarding, to have a quick sign-up and minimal paperwork. They also streamline settlements by collecting payments centrally, and automate fund transfer to merchants on a regular schedule, with its easy tracking through the dashboard.
PA handles key functions like Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, merchant management, and risk handling. They earn revenue through transaction fees and offer fast compliance and scalable solutions for merchants. Payment aggregator in India must obtain RBI approval under the PAPG guidelines, starting with in-principle approval, before full customization.
What Are the Key Differences Between a Payment Aggregator and a Payment Gateway?
This table will help you differentiate PA and PG with their features. This way, you will be able to make an informed decision.
Comparison Table (Feature-by-Feature)
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Payment Aggregator | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Merchant Account | Required per merchant | Shared under aggregator | SMBs, startups |
| Onboarding Time | Longer | Faster | Aggregator |
| Settlement | Direct | Through aggregator | Depends |
| Fees | Lower (increases at scale) | Slightly higher | Aggregator |
| PCI Scope | Full control | Minimal responsibility | Aggregator |
| Regulation | Requires own compliance | Must follow PAPG (RBI) | Aggregator |
| Technical Control | High | Moderate | Gateway |
Simplified Analogy
Payment Gateway
It can be compared to a secure bridge that safely carries your payment information from one place (Bank A/C) to the other (Bank A/C).
-
The bridge: PG is like a bridge that provides you with a secure, encrypted connection between a merchant’s website and the banks.
-
Your Car: The encrypted payment details, such as your credit or debit card number, are the car traveling across the bridge.
-
The online store’s bank will be (acquiring bank): In the end, the fund reaches their destination, where the merchant gets their payment.
Payment Aggregator Example
-
Mall = Payment Aggregator: A mall provides all stores with a centralized point to operate from. Similarly, a payment aggregator delivers you a single platform for your business to accept a wide range of payments.
-
Stores are like Individual Merchants: The stores in the mall are businesses that will need to manage their own operations and payment collections.
-
Single Checkout Counter = Aggregator’s Technology: This single counter accepts all the payments via various methods (cash, cards) for all the stores. The aggregator’s integration point does the same for different payment methods such as cards, UPI, and digital wallets.
-
Individual Bank Accounts = Individual Merchant Accounts: Ideally, every store within the mall will need to have its own bank account. A payment aggregator enables an organization to avoid opening multiple merchant accounts with different banks.
Also Read: What is Bulk Payment? Process, Benefits & Its Working?
How Each Model Works in the Payment Flow
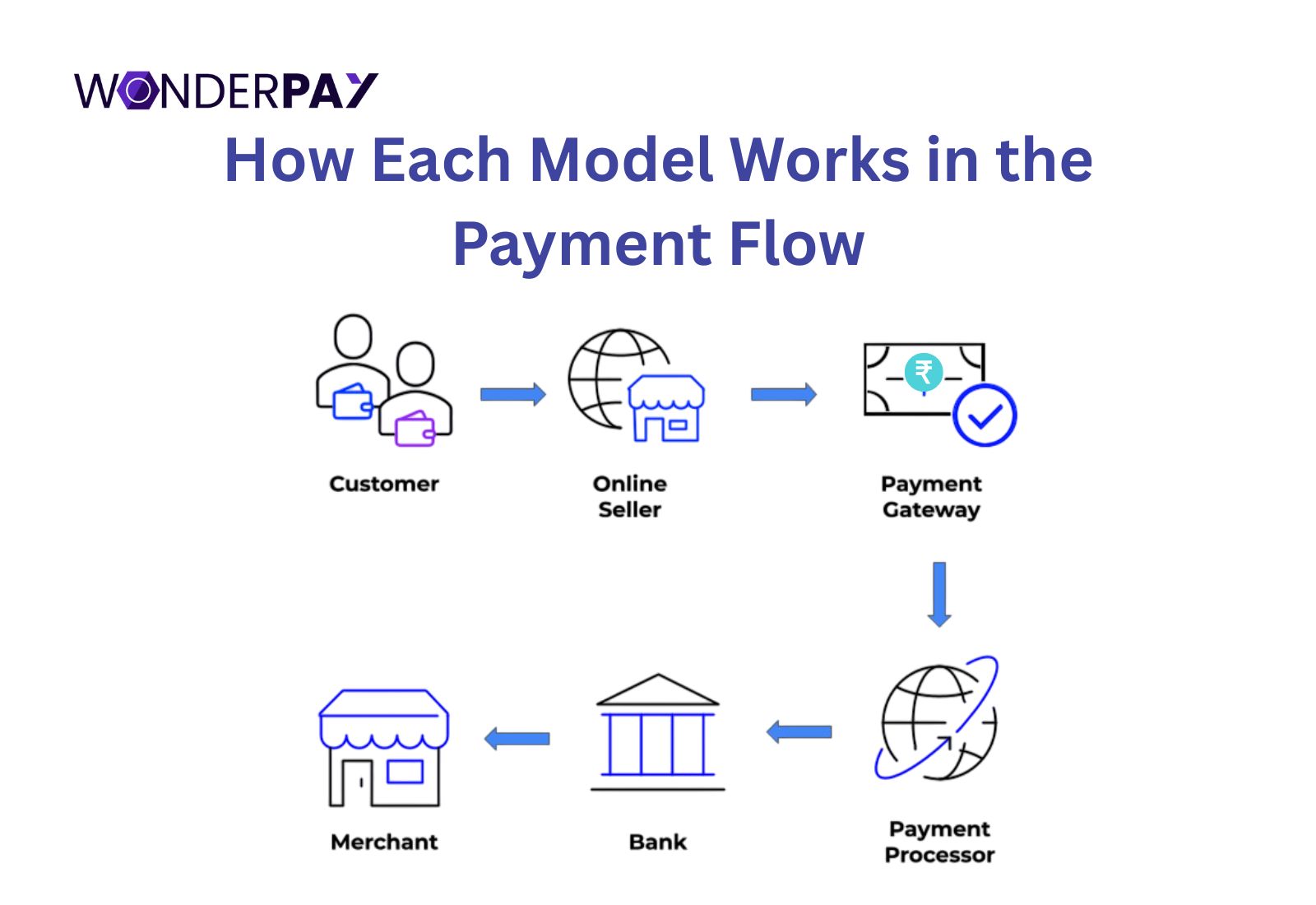
In this section, we will discuss the crucial workflow for each model. It will give you clarity for its working, for your company.
Let’s discuss all the points step by step.
Payment Gateway Workflow
1. Customer Initiates Payments
-
Customers initiate payments on the merchant checkout page after adding items to the cart.
-
The customer then chooses their preferred payment method, like card, UPI, wallet, etc. Then, enter payment details like (Card number, CVV, expiration date) on the merchant website or app.
2. Payment gateway processes transactions
-
Merchants’ system securely transmits the encrypted payment details to the payment gateway.
-
PG will encrypt the sensitive data and check it to prevent any fraud.
-
Within the 3rd step, the gateway sends translation details to the payment processor or acquiring bank.
3. Route Authorization Request
-
The acquiring bank will route the encrypted transactions info to the network of cards (payment methods), which could be any, such as Visa, Mastercard, or others.
-
Then the card network conducts further fraud checks and after that forwards the details to the customer’s bank, which will be the issuing bank.
4. Issuing Bank Authorizes or Declines
- The customer’s bank conducts a check on the cardholder’s account, verifies the available balance in the account, and performs risk assessments.
After verifying the above details, the issuer sends an approval or denial message card network and the acquiring bank.
5. Merchant Get Returned Response
The authorization response travels back through the chain to the payment gateway.
-
The response that was authorized. It will travel back via the chain to the payment gateway.
-
PG will update the merchant on the transaction status.
6. Both Customer & Merchant Get Update
-
The merchant’s system shows a status page, and at the same time shows confirmation for an approved payment.
-
Now the customer gets an SMS from their bank (issuing bank) and their account is updated accordingly.
7. Settlements and Payment Clearing
- If the payments are approved, the acquiring bank will initiate the settlement process. It involves the funds being transferred via the issuing bank to a business account.
It is a critical part that ensures the payments are settled in the receiver’s account.
Must Read: What is a Payment Gateway? Meaning, Features, and How Does It Work?
Payment Aggregator Workflow
-
The customer checks from a merchant’s website or mobile application. This request goes to the PA for the payment initiation. Now, it will direct it to the PA’s bank. Here, it verifies for a fraud check.
-
The customer chooses a payment mode, either UPI, credit/debit card, etc. Then the payment aggregator’s bank sends the request to the chosen payment mode network.
-
Now, the customer’s payment mode network forwards the request to the customer’s bank. It checks for the available balance, which would be deducted from the customer’s bank account.
Then the funds are credited into the merchant’s account. At the same time, the successful response is shown over the merchant’s web or application page, and the customer is able to check out, and the payments become successful.
Business Perspective, Which is Right for You?

What to choose: payment gateway vs payment aggregator, for your company? Selecting the right payment solution is a crucial decision for all types of businesses.
In this section, we will discuss both PA and PG’s correct use cases based on a business’s requirements.
For Mid-Size and Growing Businesses
If you are a mid-sized or a growing business. A payment gateway assists your organization with the top benefits. This will help you with the significant practices, including:
- Easy to use
- Faster setup
- Streamline management
- Businesses get complete control
- Scales your company’s growth
- Customized as you require
Example: Businesses that are scaling fast, such as software as a service (SaaS) or marketplace expanding to multiple banks. This solution from the payment gateway fulfills the gap to meet your organization’s exact requirements. It helps you accept payments with any of the payment options from the payment link, all types of cards, and Unified Payment Interface (UPI), and more.
For Enterprises and Marketplaces
You can go with the optimal choice for your organization, which is a hybrid setup. This will combine the strength of both the payment gateway and the payment aggregator. It utilizes a feature-rich aggregator.
In order to manage the full payment lifecycle, while integrating specialized gateways for specific functions, such as providing you with advanced routing or reduced costs for high-volume transactions.
For Startups and Small Businesses
The aggregator delivers a number of benefits to startups and small businesses. It is generally a better and simpler choice to begin with. PA will provide you with the following advantages for your organization.
- Quick setup with less hassle
- Wide range of payment methods
- No individual merchant A/C with the bank
- Instant onboarding
- Minimal paperwork
- Manages compliance
Example: Marketplaces Need to Have Split Settlements
-
Usually, the marketplaces handle complex payment flows, which include splitting a customer payment among multiple vendors and charging a commission. Therefore, getting started with a hybrid model will help you with the following:
-
An aggregator manages the end-to-end payment lifecycle. This includes the checkout to settlements.
-
When you use PA, you will experience that it automatically divides the total transaction amount among multiple sellers and the marketplace operators.
-
You get the best security option, such as escrow functionality. This option allows marketplaces like yours to hold the funds until delivery is confirmed, which is one of the great options for protecting both buyers and sellers.
-
You will have advanced routing, which will enable you to send high-value transactions. It can be done with the help of the direct gateway partner for potentially lower processing fees.
-
PA’s centralized management through its dashboard simplifies reporting, reconciliation, as well as vendor payments for your organization.
What Are The Best Practices for Enterprise Payment Strategy
 Implementing best practices for an enterprise payment strategy can greatly benefit you. This section prepares and provides the clarity you should have for your business.
Implementing best practices for an enterprise payment strategy can greatly benefit you. This section prepares and provides the clarity you should have for your business.
Starting with an Aggregator: You connect with an aggregator, which will help you with seamless onboarding and rapid scaling.
Specialized Payment Gateway: You can connect with a payment gateway as your transaction volume grows. This strategy will help you with high volume payments to negotiate lower rates.
Get to Use Payment Orchestrator: Getting to have a payment orchestrator. It will assist you in intelligently routing transactions by using the optimal gateway for each payment type. This will help you with cost optimization, success rate, and to have speed, which is significant as well.
Ensure Compliance: You must consider a payment aggregator that ensures all sub-merchants, including the marketplace. It must comply with the local financial regulations, significant compliance standards like Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS).
What Are the Compliance and Security Differences

When it comes to payment gateway vs aggregator for important practices like compliance and security for customers. Both differ from each other, and you must focus before you get started with a payment solution for your company.
Here, you will learn about both PA and PG solutions for your company while learning about their security patches.
PCI DSS Responsibility
-
Gateways: The top payment gateway in India, like Wonderpay, handles the complex regulations like PCI DSS. This eliminates the headache for businesses to manage all rules and regulations themselves. It means you get the freedom to focus on other valuable tasks to generate more revenue.
-
Aggregators: Many payment aggregator companies also take on compliance and security responsibilities, which then manage all transactions and the risk via their infrastructure and Merchant ID (MID).
RBI PAPG Guidelines
The digital payment entities like Wonderpay operate under the RBI’s Payment Aggregator and Payment Gateway (PAPG) guidelines. These guidelines aim to protect merchants and consumers by ensuring transparency, accountability, and the handling of funds.
The table below will clear more of your doubts with all the comprehensive points discussed in the table.
Key Regulatory Differences
| Criteria | Payment Gateway | Payment Aggregator |
|---|---|---|
| RBI Authorization | Not mandatory, and it acts as a technology service provider. | Mandatory must be authorized by the RBI to handle merchant funds. |
| Fund Handling | Gateways do not hold funds. Transactions through it settle directly from the bank to the merchant. | Aggregators hold funds temporarily before settling with merchants, as per RBI rules. |
| Merchant KYC & Onboarding | Managed by the merchant and their acquiring bank. | Handled by the aggregator, including KYC verification and transaction monitoring. |
| Settlement Timelines | Depends on the acquiring bank. | PG is governed by RBI, typically with T+1 or T+2 days. |
Pricing and Cost Comparison
 Here is the pricing and cost comparison for a gateway service provider and aggregator payment services. With this pricing structure, you will be able to know both service providers’ costs to your company.
Here is the pricing and cost comparison for a gateway service provider and aggregator payment services. With this pricing structure, you will be able to know both service providers’ costs to your company.
Fee Structure
- Getting started with a payment gateway. You will experience some payment gateway prices in the following structure:
- Some PG charges a setup fee
- Merchant Discount Rate (MDR)
- Annual maintenance
- Payment Aggregator
- Transaction-based fee (higher for low volume).
- Per transaction fee
- UPI Fees
- Merchant discount rate (MDR)
- Annual Maintenance Charges (AMC)
- Setup fees
- Settlement fees
- International card fee
Integration and Technical Aspects

When it comes to integration and the technical aspects of PA and PG. They both differ from each other after going through this section. You can make an informed decision that best fits your organization.
How Integration Differs
- Gateways: PG can provide you with both solutions. One is an Application Programming Interface (API), and another one is a plug & play solution. It delivers the benefit of having a customized solution for your organization.
It means you will have control over the appearance, such as having your own logo, color palette, fonts, etc. This will create a memorable experience for your business customers as you require with your company branding. - Aggregators: This may also help you with the plug-and-play option to integrate into your existing system, like a mobile application or website. And another way you get it is to have a low-code option for easy integration.
Reliability and Uptime Factors
Within digital payments, downtime means lost revenue for a business and trust of customers. This means choosing any of the digital payment solutions will directly impact a business’s performance.
Both solutions focus on keeping their system stable, but somehow their control levels are different. Check out the table below for more information.
| Factor | Payment Gateway | Payment Aggregator |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate Optimization | Merchants manage routing and retries across multiple banks. | Aggregators use smart routing, automatically retrying failed transactions through alternate banks or methods. |
| Downtime Management | Merchants receive API alerts or manual updates from banks. | Aggregators provide real-time notifications and status dashboards for uptime visibility. |
| Performance Benchmark | 98 to 99% success rates, depending on bank infrastructure. | Almost the same (99%) success rate with auto-retry logic and fallback routing. |
What is the importance of UPI and 3D secure testing?
The 3d Secure and UPI are the backbone of online payments in India. They play a crucial role and must be tested for real-world reliability as quickly as you decide to go live.
UPI Testing: Validate intent flow, collect flow, and fallback to alternate Payment Service Provider (PSPs).
3D Secure Testing: Simulate one-time password (OTP) delays, authentication timeouts, and issuer failures.
Local Testing: You can check and ensure that its performance is good under peak volumes like festive sales.
FAQs: Quick Answers
-
What is the main difference between a payment aggregator and a payment gateway?
The payment aggregator’s meaning can be defined by its role, as it is a service that consolidates multiple merchant accounts into one and handles both the transaction data flow as well as actual funds. A Payment gateway works as a bridge between a business and its customers for digital payments. It securely transmits payment data.
-
Which is better for startups, a payment gateway or a payment aggregator?
It is upon your needs. For some startups, an aggregator may fit because it offers simple, faster onboarding, reduced compliance. On the other hand, a gateway could be a good choice for high-volume companies that need more control, customization, and direct relations with acquiring banks.
-
Do aggregators need RBI approval?
Yes, every non-bank payment aggregator needs authorization from the Reserve Bank of
India (RBI), but it does not apply to banks, as they already carry a bank license. The non-bank entities must apply for an authorization while meeting the net worth criteria and comply with various RBI guidelines to operate legally. -
How long does the settlement take in PG and PA?
The settlement cycle for both gateway and aggregator typically ranges from T+1 to T+3 business days. However, many providers like WPay offer faster options T+0 (instant settlements), often for an additional fee.
-
Can I use a payment gateway without a payment aggregator?
No, usually a gateway requires an aggregator as it needs a merchant account to process transactions. On the other side, the role of a gateway is to provide technology for secure payment transaction data between merchants and customers’ banks for the purpose of successful transactions.
-
Do payment gateways and payment aggregators have security features?
Yes, they both provide security features such as encryption, fraud detection, and compliance with standards such as PCI DSS to secure customer card details by tokenizing. The gateways focus on securely transmitting payment information, and PA manages the flow of funds and compliance for multiple merchants.
-
Can a business use both a payment gateway and a payment aggregator?
Yes, they both can be used, and they work together. Payment aggregators and Payment gateways both allow businesses to get advantages from the aggregator’s convenient, one-stop shop approach and managing multiple payment methods, as well as handling compliance.
Final Thoughts
Hope payment aggregator vs payment gateway is clear to you now. However, choosing the right solution for your organization requires careful consideration. Because it should meet your company’s exact requirements, the budget you have set from maintenance to setting up the solution, etc.
Both the gateway and aggregator have unique benefits based on scale and control needs for an organization. Before you start with one, know your business’s needs and requirements first. This will help you choose the right solution for your company as needed.
If you are in search of a reliable digital payment solution for your organization. Wonderpay is your one-stop solution for your business. We handle everything from security patches, compliance, to guidelines. I mean no headache for the business-savvy at all, and they can just focus on growing their business. Connect with us right now, and get your custom payments consultation for free.





