- 1. What Is a Merchant Payment?
- 2. What Is a Payment Gateway?
- 3. What Is a Merchant Account?
- 4. How Payment Gateway and Merchant Account Work Together?
- 5. The Trend: UPI Merchant Payments vs Card Payments?
- 6. Merchant Payment Apps vs Full Payment Gateways
- 7. Payment Gateway vs Merchant Account Comparison Table
- 8. How Wonderpay Simplifies Merchant Payments for MSMEs?
- 9. Summary
- 10. FAQs
The digital merchant payment acceptance is easy, but understanding how money moves is not. It often confuses organizations about the merchant payment gateway vs merchant account. This confusion does not clarify the picture regarding where their payments will occur, what if their payments are delayed, and the uncertainty about transaction visibility.
The confusion usually causes business decision makers to select the wrong gateway. It could let merchants face hidden payment settlement prices and compliance risks.
This guide breaks down what a payment gateway is and how merchant accounts actually work.
Let’s get the ball rolling!
What Is a Merchant Payment?
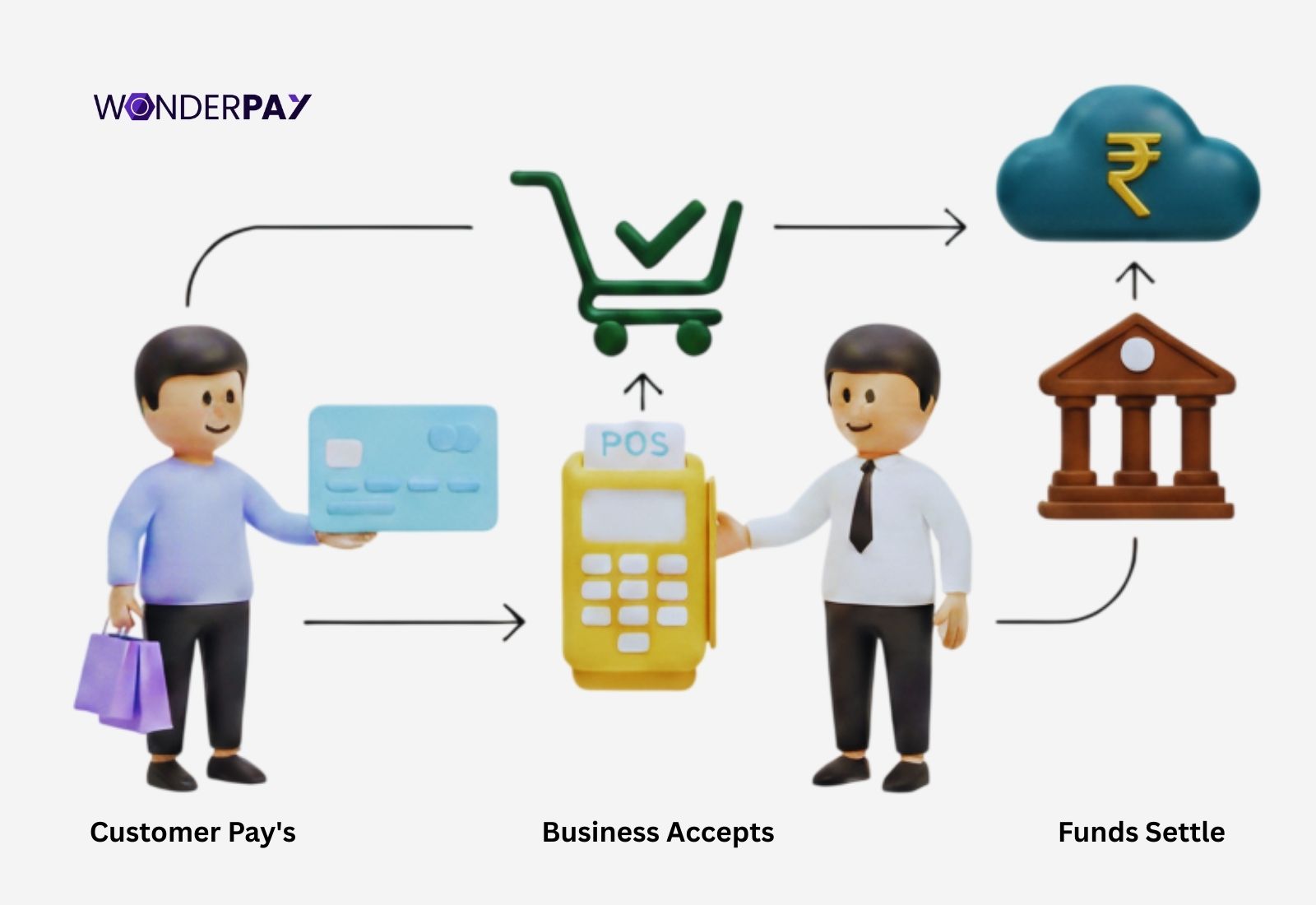 The merchant account meaning a tool that is unlike your normal bank account. A merchant account is created for businesses by financial institutions, such as a payment gateway. In order to receive a business’s online payment via multiple payment channels like Netbanking, credit or debit cards, UPI, etc. It also allows you to get in-person payments using a Point of Sale (POS) machine.
The merchant account meaning a tool that is unlike your normal bank account. A merchant account is created for businesses by financial institutions, such as a payment gateway. In order to receive a business’s online payment via multiple payment channels like Netbanking, credit or debit cards, UPI, etc. It also allows you to get in-person payments using a Point of Sale (POS) machine.
In your normal bank account, you keep money securely on a regular basis either by receiving from someone (friend, family, earnings, etc) or credited by yourself.
A merchant payment account enables them to accept payments from customers in exchange for goods or services. The payment transaction can be facilitated using multiple channels, such as digital wallets, card transactions, and bank transfers.
In order to accept merchant payments online or in-person (in-store), companies heavily rely on financial technologies like payment gateways, including acquiring banks, to process, authorize, and settle payments smoothly.
A Real-Life Merchant Payment Example
Suppose you sell clothes online via an e-commerce website. Customers land on your website, select an item, and proceed to the checkout page. The customer chooses a payment method, such as a card, to make a merchant transaction.
The customer fills payment details, makes a payment, and you get a payment credited notification, and the customer sees a payment successful message for the merchant payment. Behind this scene, there is a secure payment service provider that facilitates payments, first checks for balance availability (insufficient and sufficient balance), authorizes, encrypts payment data, and shows notification to both the payment receiver and buyer, either for a successful transaction or a failed one.
What Is a Payment Gateway?
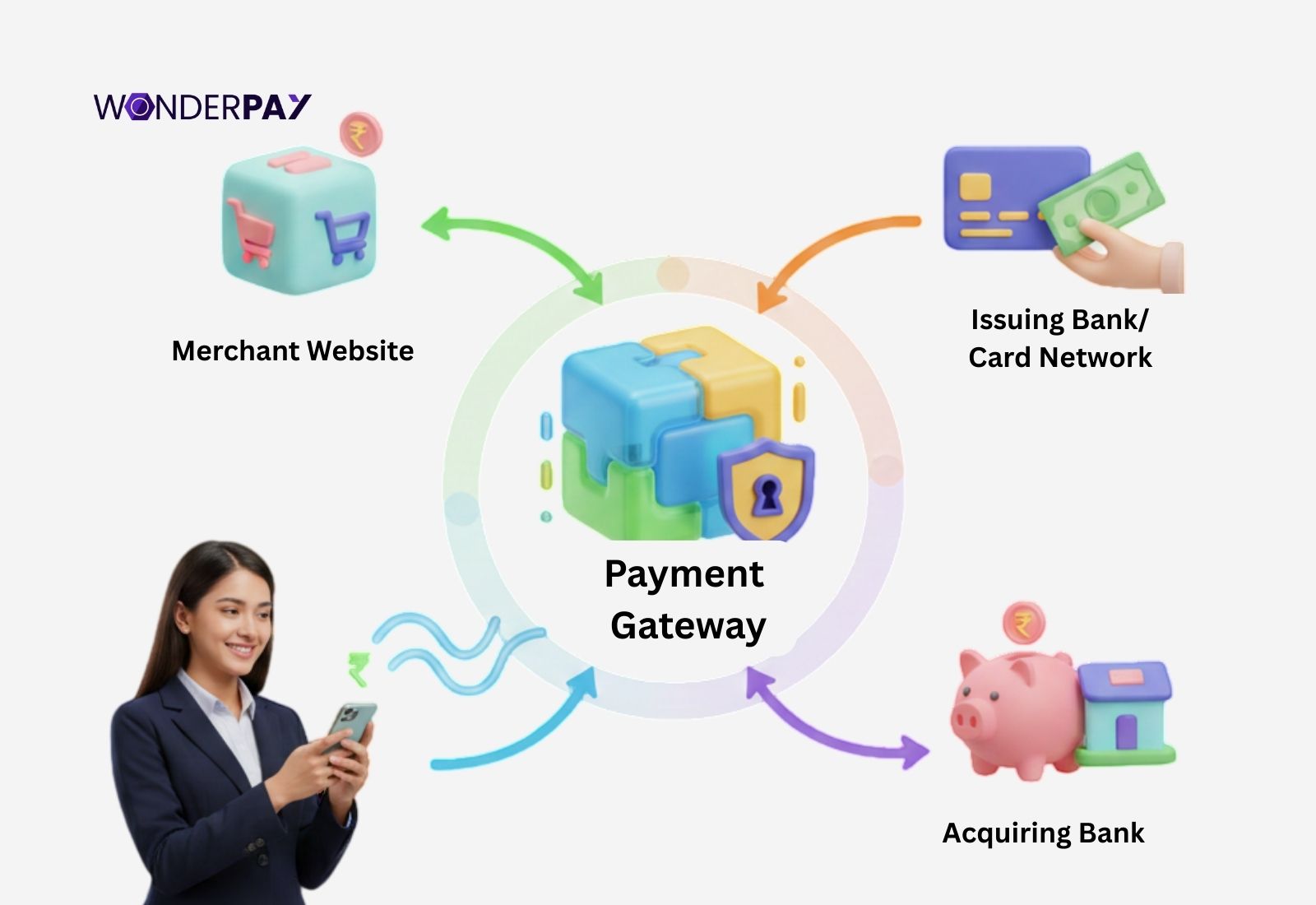 It is a secure technology that acts as a digital track to connect merchants’ websites or mobile applications to banks and payment networks. In order to process online payments, such as credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and UPI.
It is a secure technology that acts as a digital track to connect merchants’ websites or mobile applications to banks and payment networks. In order to process online payments, such as credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and UPI.
Role of a Merchant Payment Gateway in Online Payments
A merchant payment gateway plays an important role in securely capturing, encrypting, and transmitting customer payment data (cards, wallets, UPI), while verifying funds and authorizing the transactions and then confirming the transaction back.
The best part of a payment gateway is that it enables businesses to get online payments safely, supports multiple payment methods, prevents fraud, and functions like a digital POS system for e-commerce.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor
A payment gateway acts like a vehicle that carries payment information securely from the customer to the financial system. A PG encrypts sensitive payment details and transmits them safely for authorization.
A payment processor, on the other hand, is the engine working behind the scenes. It handles transaction authorization, communicates with issuing and acquiring banks, and facilitates the movement of funds until the payment is approved and prepared for settlement.
Also read: What is a Payment Gateway? & How Does It Work?
What Is a Merchant Account?
It is unlike a standard bank account, especially created for merchants (businesses) to accept customer payments, with payment methods like credit, debit card, netbanking, UPI, or other electronic payment methods.
In India, merchant accounts are facilitated by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) authorized payment aggregators or acquiring banks as part of the merchant onboarding process. Businesses seeking a merchant payment gateway must complete Know Your Customer (KYC) and submit the required payment gateway documents to comply with RBI regulations.
A merchant account acts as an intermediary settlement layer. The funds collected from customers are temporarily held in RBI mandated escrow accounts (in the case of payment aggregators) or designated merchant nodal accounts (in the bank led models). These accounts ensure regulatory oversight, transaction monitoring, and dispersed management.
The fund transfer from the merchant account to the company’s main bank account usually takes T+1 or T+2 working days. This settlement cycle allows for transaction reconciliation, risk check, chargeback handling, and regulatory compliance, which protects both the merchants and customers.
Merchant Account Examples
Who does a customer buy daily grocery items from? A nearby store, a supermarket, by visiting in person, or a quick e-commerce store online like Bigbasket, Swigy, etc. (they are all merchants), right? These grocery service providers have a merchant account created by a payment service provider.
The time a customer selects the items, initiates a merchant transaction by redirecting to the checkout page. The customer fills in payment details by selecting after selecting a preferred payment method.
The entire payment process is completed with the help of a payment gateway (online payment service provider), which provides a merchant account to businesses for a smooth payment experience.
How Payment Gateway and Merchant Account Work Together?
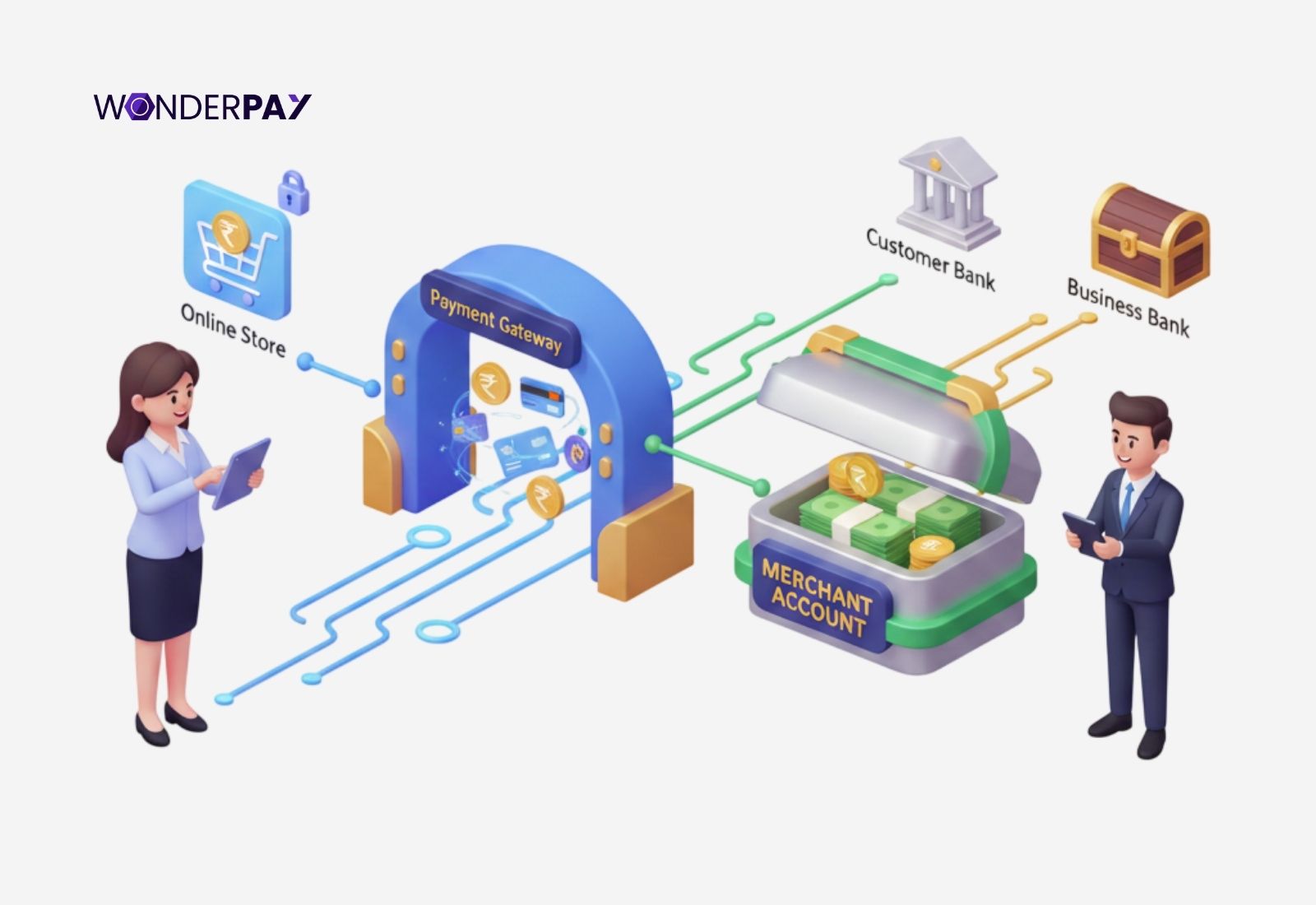
First of all, let us discuss both a merchant account and a payment gateway. This will help us get a better understanding of both the systems before directly jumping to the merchant payment processing with the combination of the gateway and merchant bank account.
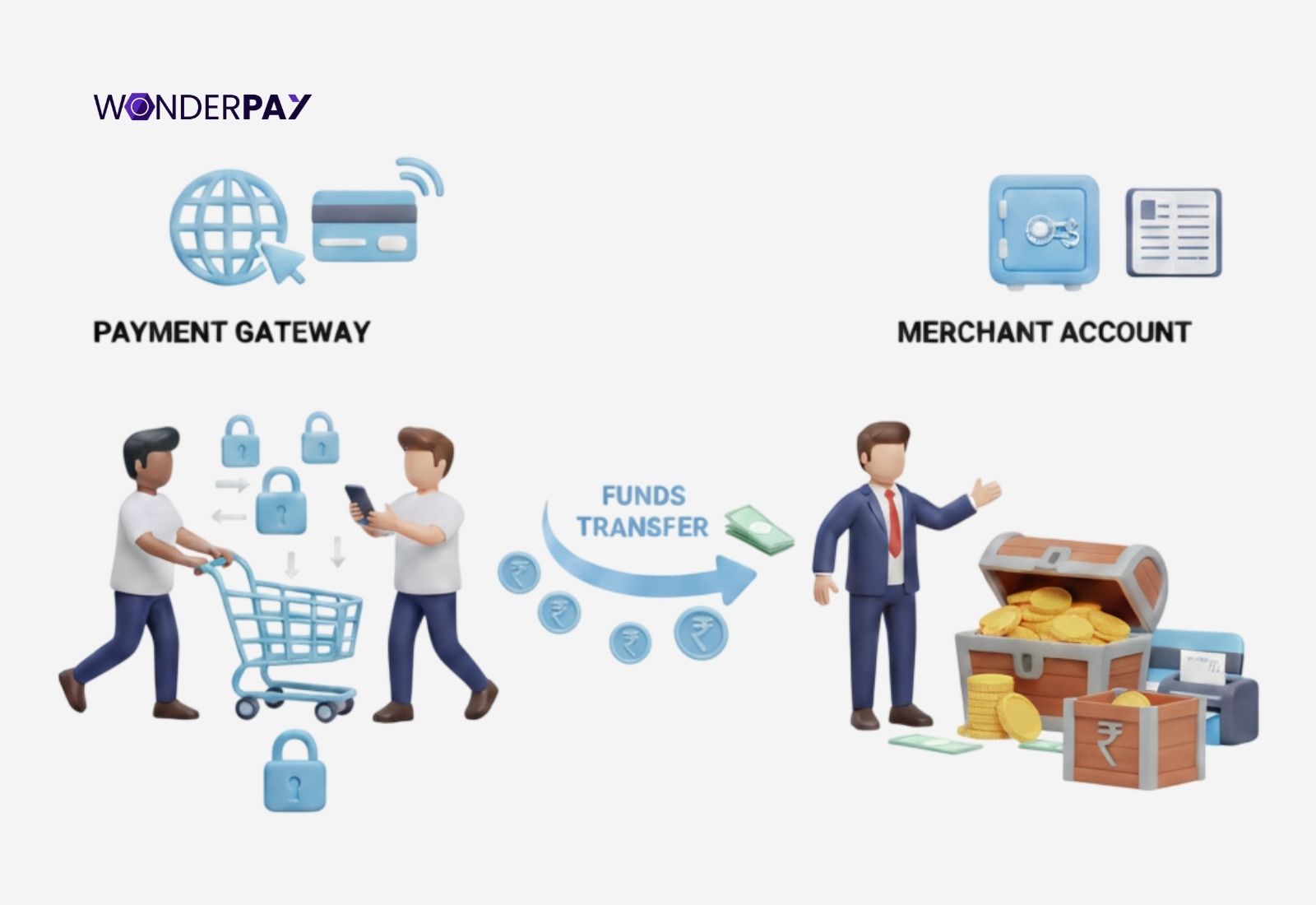
A payment gateway and merchant account are both separate, significant components within a gateway infrastructure. With different roles gateway is a technology. It acts as a secure, virtual point of sale terminal, which encrypts customer data and communicates with banks while authorizing transactions.
A merchant account, on the other hand, is a holding account. It is a specialized banking account; its role is to hold funds after a translation is authorized by the gateway communication with banks, before the payments take place in a regular business bank account.
Step-by-Step Merchant Transaction Flow
Here is how gateway and merchant accounts work together for a successful online payment merchant needs.
-
Checkout: After selecting items or buying a service. The customer enters payment details on the website.
-
Encryption and Routing: The merchant payment gateway encrypts payment data and securely forwards it to the payment processor.
-
Authorization: Now payment processor connects to the payment issuer bank. It approves or declines a transaction by checking the sufficient or insufficient balance.
-
Confirmation: Based on the authorization process gateway shows a payment successful approval or decline notification back on the merchant platform website or mobile application to complete the purchase.
-
Settlement: If everything goes accurately, then the fund is transferred from the customer’s bank account to the merchant account. Here, the merchant can see every payment detail clearly.
-
Settlement: Now the settlement happens as mandated by the RBI on T+1 or T+2 from the merchant account to the business’s regular bank account.
Suggested Read: How To Choose Best Payment Gateway In India For SaaS
The Trend: UPI Merchant Payments vs Card Payments?
UPI Merchant Payments In 2026
The trend of Unified Payment Interface (UPI) is increasing at a rapid rate in India. According to recent reports, The Economic Times UPI processes over 20 billion transactions a month, and it accounts for roughly 85% of the country’s digital payments.
UPI merchant payments involve an instant debit from the customer’s bank account, but the settlement to the merchant does not happen instantly. Once the customer authorizes the payment, the transaction is routed through NPCI’s UPI infrastructure, which validates the request and coordinates with the issuing and acquiring banks.
Although the payment confirmation is immediate, the funds are settled into the merchant’s bank account later. It will be the same as usual, as a T+1 working day, which is one day after reconciliation and compliance checks. This settlement structure ensures transaction traceability, dispute handling, and regulatory oversight for both customers and merchants.
Card Payments in 2026
On the other side of the coin, the card payments in 2025 and 2026 have also improved. Now, card payments allow linking credit cards with UPI. It is a big move, which endorses digital payments for both cards and UPI.
This significant move helps customers make online or in-person purchases easy. Business customers can make merchant payments using the same UPI PIN. UPI payments are already simplified. Card payments will continue to rise, which is great as it offers exciting perks to the buyers, such as booking air tickets, purchasing products, booking shows, and much more.
The industry in India witnessed a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% in the first five years. The number of users increased rapidly and crossed 78 million. The overall spending using the credit card reached its highest of 1.3 lakh crore.
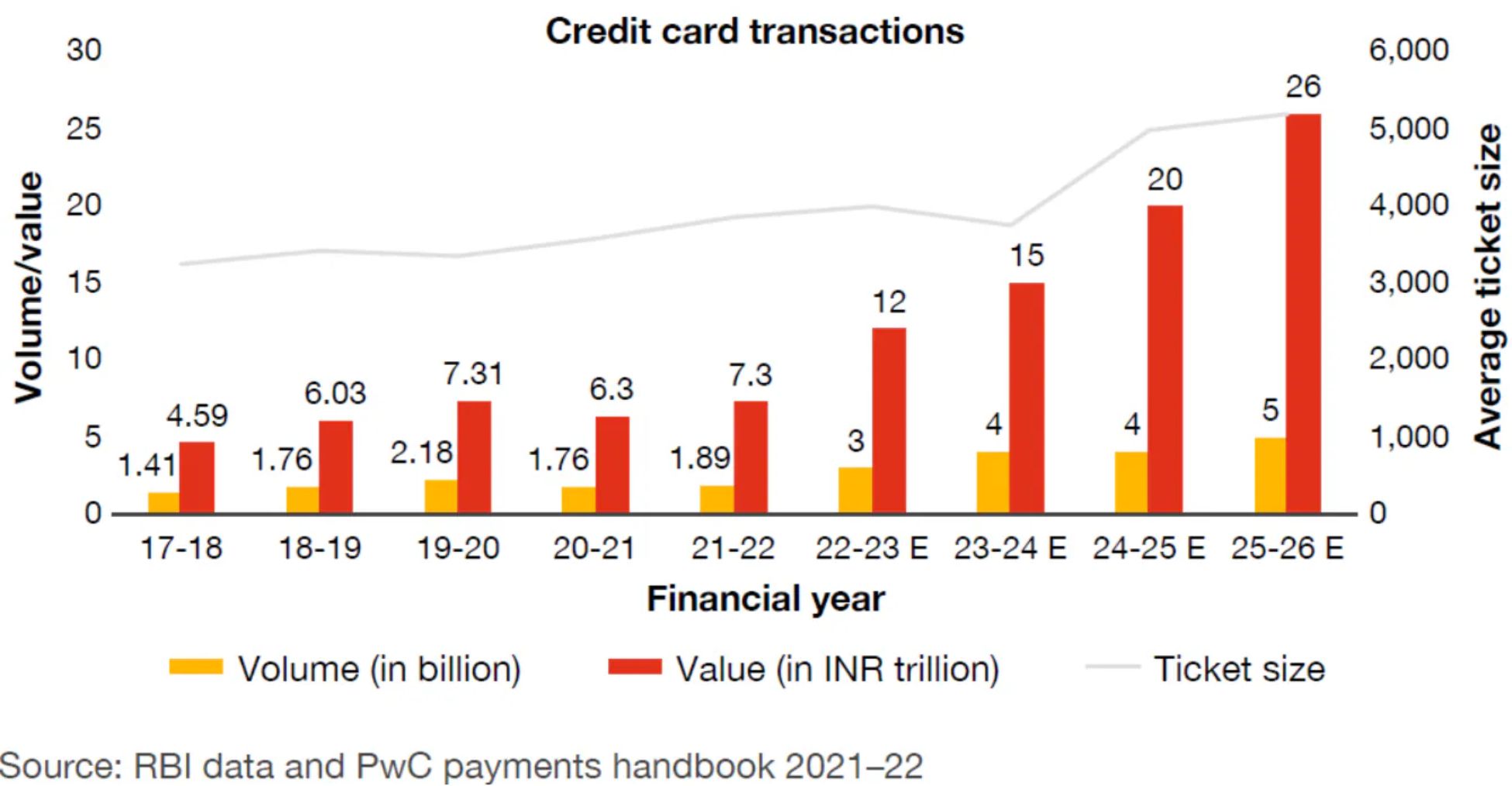
Graph source: PwC
As shown in the graph, it indicates that the total value of credit card transactions is expected to reach around INR 26 trillion by the financial year (FY) in the current year 2026, while the average ticket size is projected to increase to approximately INR 5,000 to 6,000 per transaction.
How Online Payment Merchants Get Paid: Know The Basics?
It depends on what kind of online payment method the customer uses. Whether the customer chooses UPI, credit, debit card, or old net banking. The payment flow is a little different, but the way the cash gets to the merchant is pretty much the same. It provides instant confirmation, yes, but do not expect the cash to arrive right after the merchant payment is made.
UPI: It allows customers to pay using an application login and make payments with just a secure PIN. The payment is debited from the customer’s bank account immediately, but does not settle in the business’s regular bank account.
Cards (Credit/Debit): A buyer fills in card details, payment process happens from authorizing payments to crediting the merchant account. It usually requires One Time Password (OTP) or two factor authentication (2FA).
Net Banking: the customer gets shunted off to their bank, makes the payment, and then the cash gets settled once the reconciliation numbers are crunched.
It does not matter what method the customer uses; all payments go through that payment gateway first, then get settled to the merchant’s bank account in accordance with the RBI guidelines for payment settlement guidelines within 1 to 2 days.
Must Read: Instant Settlement Payment Gateway In India: Complete Guide
Merchant Payment Apps vs Full Payment Gateways
A merchant payment app and a full payment gateway distinguish each other with their average token size, needs, stages of growth, and business type. Although both of them enable merchants to accept online payments.
When to Use a Merchant Payment App?
It is the best option for small offline merchants. The application software provides a plug and play solution, with no technical knowledge or learning needed at all, and small businesses like small cafes, street food vendors, and more can accept payments in-person using just an unique QR code.
The ease of digital payments with a merchant payment app allows both merchants to accept and customers to pay on the go securely. It does not need a street vendor to get online payments, build a website to integrate a payment solution, pay any scheduled fees, maintenance, or heavy compliance.
When You Need a Merchant Payment Gateway?
A merchant payment gateway like Wonderpay comes with a complete payment infrastructure. It is designed for startups, SaaS companies, e-commerce businesses, marketplaces, and platforms. A full gateway solution allows you to accept payments using all payment methods.
Gateway solutions enable your company to use them in several ways, including integrating the solution within your company website, mobile application, the checkout flow via Application Programming Interface (API), & Software Development Kits (SDKs), and get all your payments via multiple payment methods (UPI, cards, net banking, wallets).
Additionally, merchant payment gateways are highly scalable and customizable as required, compared to merchant payment apps. A PG solution, such as Wonderpay, grows simultaneously with your business.
The best part of a payment gateway in India is to opt for rich features like invoice financing via the Trade Receivable e-Discounting System (TReDS). Means MSMEs can easily get working capital for smooth business operations.
Must Read: Best Payment Gateway for Freelancers & Creators in India
Payment Gateway vs Merchant Account Comparison Table
 This clear comparison table for both merchant payment gateway and merchant account will assist you in differentiating between them. Here is comprehensive information for both to help you make an informed decision in choosing a gateway that aligns with your business requirements.
This clear comparison table for both merchant payment gateway and merchant account will assist you in differentiating between them. Here is comprehensive information for both to help you make an informed decision in choosing a gateway that aligns with your business requirements.
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Merchant Account |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Securely captures, encrypts, and transmits customer payment details for authorization. | Temporarily holds customer funds before they are settled into the merchant’s main bank account. |
| Who provides it | Offered by RBI-authorized Payment Aggregators or banks as a technology service. | Facilitated by acquiring banks or RBI-authorized Payment Aggregators as part of merchant onboarding. |
| Settlement time | Does not handle settlement directly; it enables payment authorization in real time. | Funds are typically settled to the merchant’s bank account within T+1 or T+2 working days. |
| Compliance | Must comply with RBI guidelines, PCI DSS standards, and data security requirements. | Governed by RBI regulations, including escrow or nodal account rules and KYC obligations. |
| Cost | Charged as transaction fees, setup fees, or platform usage fees. | Costs may be bundled with gateway fees or included as part of the overall payment service. |
| Best for MSMEs | Businesses that need to accept online payments through websites, apps, or APIs. | Businesses that want regulated, transparent settlement and secure handling of customer funds. |
How Wonderpay Simplifies Merchant Payments for MSMEs?
A merchant payment gateway, Wonderpay, delivers a simplified solution for Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). It offers organizations the top gateway service, which includes account handling together, prioritizes security by putting compliance first, so you are not stuck to clear mandatory compliance like PCI DSS and RBI regulations.
WPay’s transparent settlement makes it easy for your organization to work on more complex tasks by eliminating repetitive tasks like reconciliation, frequent payments, preparing reports, and detecting customer behaviour to improve services with its automation.
Also Read: Why Choose Wonderpay Payment Gateway In India for Businesses
Summary
Now the difference between a payment gateway and a merchant account is clear to you. The guide helps you distinguish what each component’s role is in merchant payments. At the end, we learned both work together, one enables businesses bank (acquirer bank) and the customer bank (issuer bank) to communicate, authorize payments, and shield by encrypting payments. And the other holds the fund while protecting both the customers and merchants by avoiding the disputed transactions.
Both payment gateway and merchant accounts are crucial for businesses seeking a digital payment solution.
If you are in search of a reliable, trusted, compliant, and the top payment gateway service provider in India. Do not hesitate to connect with one of our representatives to consult with you for free. Connect right now and endorse your business growth.
Suggested read: Future of Payment Gateways in India
FAQs
1. What is merchant payment?
The meaning of merchant payment is collecting funds for the sold services or products in person or online. Ex. you went to a nearby store to buy groceries after selecting and packing all the things you bought. You go to the counter for billing, suppose your total amount was Rs. 2000.
The store owner gives you a QR code to scan for UPI payments, or a POS for card payments, as you choose, and you make payments. This process of collecting payments from customers by a business online or offline (in-person) is called merchant payments.
2. What is a merchant account?
A merchant account meaning a place where a merchant’s payments land after a customer pays, regardless of payment channels (UPI, netbanking, cards, and more). A merchant account is like a bank account, created at the time of seeking online payment services by any financial institution. It could be a payment gateway and a bank offering financial payment infrastructure to accept or disburse electronic payments securely for any purpose.
3. What does a merchant transaction means?
It is a kind of online fund transfer process that includes customers, the merchant’s suppliers, and stakeholders. The merchant transaction includes both accepting payments from customers and disbursing them among the supplier and stakeholders. The transactions can be for any purpose, either for selling products/services, making payments like giving salaries to the employees in bulk, initiating bulk cashbacks, and more.
4. What is the difference between a payment processor and a payment gateway?
A payment processor and a payment gateway both are different from each other. A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates online transactions by acting as a digital bridge between customers and merchants. It encrypts customer payment data on a website, while a payment processor acts as the backend engine to let the payment data route between banks, both customers and businesses. In order to authorize and settle the transaction for a seamless experience.
5. Is a merchant account required in India?
Yes, it is mandatory by the RBI to have a merchant account. If you want to accept merchant payments via any electronic payment method, such as credit/debit cards, digital wallets, etc., from your customers directly on your platform, like a website, app, or at a physical store. A merchant account will act as an intermediately account for your company to hold the collected funds from customers before they are settled in your regular bank account.
6. Can I use a payment gateway without a merchant account?
No, every merchant must have a merchant account. At the time of seeking a payment service to accept merchant payments or disbursements. In case a vendor/merchant does not open a payment account, they can not use a payment service for their business under any circumstances. It is due to the rules and regulations by the authorized body of India, the RBI.
It asks payment service providers to onboard a merchant only after a careful KYC process verification with all the accurate documents required for payment gateway onboarding in India.
7. How long does settlement take?
A merchant payment fund settlement only happens after T+1 or T+2 days. Your collected funds in the merchant account are transferred to your standard bank account as set by the RBI mandatory regulations. This compulsory process ensures that the funds collected are not disputed amounts.
8. Are merchant accounts safe?
Yes, merchant accounts are 100% safe due to high security and compliance practices mandated by the Reserve Bank of India. The first thing financial institutions or payment service providers do is to verify one’s identity before onboarding with the KYC documents required, PCI DSS to shield customer payment data. This makes it a strong system to protect merchant accounts. It means both the customers and the merchants are safe to use the digital payments via a compliant payment service provider.
9. What is the cost difference?
The cost difference can refer to a payment service provider’s fee on each transaction, which is often specific to a payment method used by a customer, and varies from one payment service provider to another. The cost can be customizable sometimes, differ for cross borders, and less for payment methods like UPI.